Cacao Tree to Cacao Paste
December 14, 2020Organic Food Logistics – How do organic food products travel across the globe?
May 10, 2021For some years now, we´ve rapidly grown in awareness of what we put into our bodies and what we feed our families. There are many different factors now that play out when we are trying to decide for a product. One of the most important ones we should consider is a food safety certificate.
What is a Food Safety Certificate?
Food safety certificates tell you not only about the specific qualities and characteristics of a product, but they are also a way to ensure that the organizations involved in the development of the product, from the farm or plantation all the way to your local store shelf, meet a very high standard of quality regarding different factors like hygiene, machinery and equipment, technology, IT systems, microbiological testing, managerial practices, fair trade, fair human resource compensation, packing and transportation procedures, etc.
These certificates bring certainty that the farmers, manufacturers, handlers and retailers of the food products have set up systems that allow them to prevent, mitigate and control any possible risk involving the products, and that they have taken every precaution in compliance with international standards to guarantee the quality and safety of the product to the consumer.

HACCP
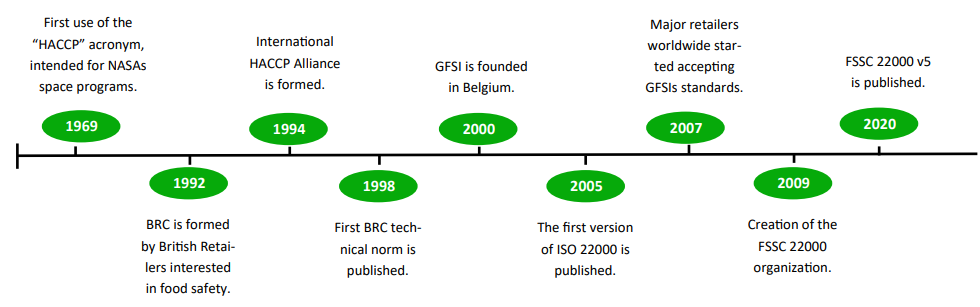
The first attempts to create a standardized food safety system were carried out in the 1960s, when the US Army, along with NASA and Pillsbury, a private company were looking to design the first food guidelines for space flights. In 1969, the term HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point System) was used for the first time, when Pillsbury submitted their program to the FDA for approval. When the International HACCP Alliance was established in 1994, it´s initial mission was to assist the meat and poultry industry with the implementation of the system. Today, it´s memberships spread all over the professional and industrial areas related to the food industry.
The HACCP was thought out as a systematic way to analyze and control safety hazards within the food industry. It´s main component are 7 principles that allow for a reliable and trustworthy operation: First there is a hazard analysis to determine Critical Control Points (CCPs), then critical risk limits are established as well as procedures to monitor those limits, there is also a plan with corrective actions in case any hazard materializes during the process. This process is constantly being reviewed through previously established verification procedures, and every stage of the process is archived and kept under the record-keeping and documentation procedures. It has been recognized by the GFSI as a cornerstone of standardized food safety programs.

BRCGS
The British Retail Consortium was established in 1992, and it is formed by most retailers in Great Britain: from family-owned stores to large supermarket chains. Upon the agreement that the food safety assurance was a convenient thing for the entire retail industry, they started working on the first drafts of a system that would standardize food safety along Great Britain in 1996. This system was first published in 1998, and now the BRC Standard Technical Guideline is followed by over 25,000 companies in 130 countries.
The BRC was designed to bring accountability and traceability to the entire supply chain, and that is one of the reasons it relies so heavily on the HACCP criteria, as well as the ISO 9001 standard, making one of the most popular options when looking for an overall certification that ensures food safety as well as best management practices. In 2019, the BRC was rebranded to BRCGS, although it has been a GFSI compliant certification for quite a long time now.

FSSC 22000
Another one of the most common certifications worldwide is the FSSC 22000 (Food Safety System Certification 22000), which was established in 2009 to help organizations set and continuously improve the control and management of food safety. The FSSC 22000 certification scheme is governed by a non profit organization, and monitored by an independent advisory committee.
The process to obtain the certification is thorough, composed by three main requirements: ISO 22000 standards have to be met, as well as PRPs (sector specific Pre-Requisite Programs), and some additional FSSC requirements that allow for consistency and integrity, and also provide governance to the organization. Over 25,000 companies have certified their operations through the FSSC 22000 program worldwide, and it is also a GFSI compliant certification.
GFSI
The Global Food Safety Iniciative is a global effort led by the International Trade Organization, established in 2000. Its main objective is to benchmark food safety certifications and programs across the world and provide a reliable reference platform for safety, quality and management procedures, thus elevating the level of accountability in the food industry and helping companies deliver high quality products to the end consumer.
GFSI oversees a large number of food safety certification programs, and sets requirements for them to comply with international standards. Some of the GFSI recognized and benchmarked schemes are:
- BRCGS (British Retail Consortium Global Standards)
- FSSC 22000 (Food Safety System Certification 22000)
- IFS (International Featured Standards)
- SQF (Safe Quality Food)
- JFSMA (Japan Food Safety Management Association)
- Global GAP (Global Good Agricultural Practices)
- Primus GFS (Primus Global Food Safety)

How are the BRCGS and the FSSC 22000 programs different?
Although both programs are GFSI certified, there are some differences between the two. One of the differences is that the BRC standard focuses on quality, food safety and compliance, whereas the FSSC 22000 is more focused on food safety and compliance. Also, regarding food safety, the BRC has very clearly stated requirements regarding hygiene that have to be followed, while the FSSC 22000 offers more of a framework to develop a food safety program specific to your own organization. Besides that, BRC requires an on-site audit, where the FSSC 22000 program requires two of them.
They are both GFSI recognized programs, and they are both generally accepted all over the world. They are also two of the most popular certification programs globally, with over 50,000 companies certified between the two of them. Both of them are very well known programs in the industry, they have very thorough requirements to be met, and they have remained at the forefront of food safety for many years now.
What is the difference between ISO 22000 and FSSC 22000?
The ISO 9000 is a group of different quality management system certifications, of which the ISO 22000 is derived from. This ISO 22000 is a quality management certification focused on the food industry, as one of its main components are the HACCP guidelines, as well as some other requisites, but it is not a GFSI recognized standard. On the other hand, the FSSC 22000 standard is based on the ISO 22000, as it also takes into account the HACCP criteria, but has the PRPs and additional requirements mentioned before, so it makes it GFSI compliant. That is the main reason the FSSC 22000 is one of the most popular food certificates worldwide nowadays.
So how do I make the right choice?
Depending on the origin of the product you buy, you may find that they come with a certain food safety label, although this label may not always be GFSI recognized. For the consumer, buying products certified by GFSI recognized programs, such as the BRC or the FSSC 22000, ensures that every single actor in the supply chain, from farm to table has met the highest standards available in food safety today.
At Maretai Organics, we understand the value of consuming high quality/low risk products, and that is why we have partnered with top suppliers, carriers and retailers globally, who share our vision for making sustainable and safe, high quality food products available to you all over the world. We take pride in taking care of our customers, not only from the moment they reach out to us, but long before, from the moment their future product starts to germinate from the ground up.
Resources
HACCP guidelines: https://www.fda.gov/food/hazard-analysis-critical-control-point-haccp/haccp-principles-application-guidelines
BRC: https://www.brcgs.com/our-standards/consumer-products/
FSSC 22000: https://www.fssc22000.com/about-us/
GFSI: https://mygfsi.com/what-we-do/race-to-the-top-framework/



